Human Resource Planning (HRP) is a vital process that aligns an organization’s human capital with its strategic objectives. This alignment is crucial for achieving organizational success, as effective HR planning ensures that the right people are in the right roles at the right times. Companies that excel in HR planning not only optimize their workforce but also gain a competitive advantage by being proactive in addressing workforce needs.
Research indicates that organizations with robust HRP practices are better equipped to navigate challenges and capitalize on opportunities. For instance, a study by the Work Institute found that 78% of voluntary turnover could have been prevented through timely interventions by employers. This highlights the importance of HRP in fostering employee engagement and satisfaction, ultimately driving improvements across the organization.
What Is Human Resource Planning (HRP)?
Human Resource Planning (HRP) is the process of ensuring a company has the right people, with the right skills, at the right time. It helps businesses plan for future staffing needs, fill skill gaps, and make sure employees are ready to support the company’s goals. This involves analyzing current workforce capabilities, predicting future requirements, and implementing strategies to bridge any gaps.
HRP encompasses various activities, including talent acquisition, training and development, succession planning, and workforce planning optimization. By proactively managing these elements, organizations can ensure they have the necessary skills and capabilities to achieve their hr strategic goals.
Key Objectives of HRP
Ensuring Optimal Use of Human Resources
HRP aims to maximize the efficiency and effectiveness of the workforce by aligning talent capabilities with organizational goals.
Bridging the Gap Between Current Workforce Capabilities and Future Business Needs
By identifying skill shortages and surpluses, organizations can better prepare for future demands.
Reducing Risks Related to Talent Shortages or Surpluses
Proactive HRP helps mitigate risks associated with fluctuating workforce demands, ensuring business continuity.
The HRP Process
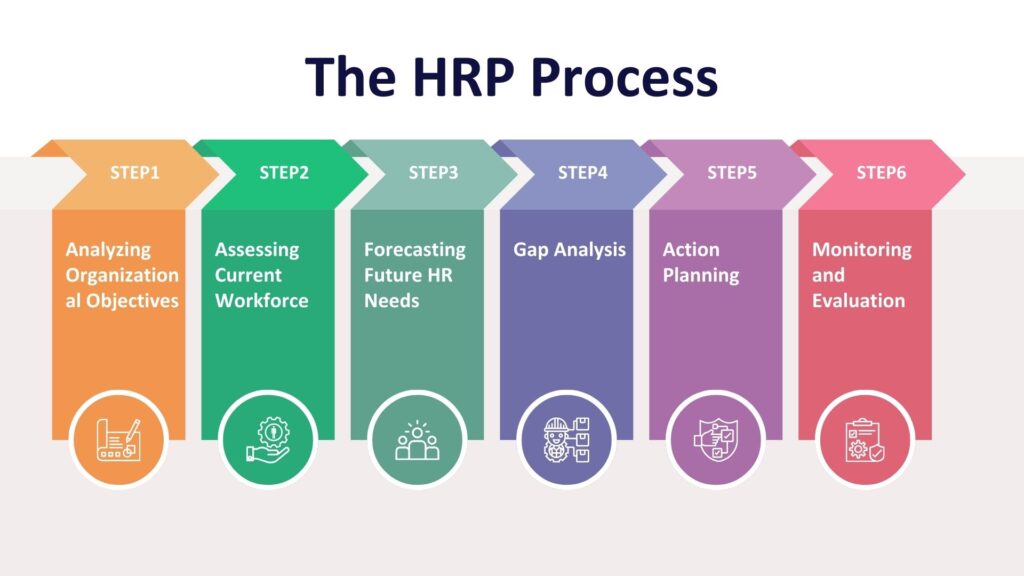
The HRP process is systematic and involves several key steps:
- Analyzing Organizational Objectives: Understanding business goals and growth strategies is essential for effective HRP. This step involves engaging with leadership to clarify hr strategic priorities.
- Assessing Current Workforce: Conducting a skills inventory and performance reviews helps identify existing capabilities. This assessment should include evaluating employee skills, experiences, and potential for growth.
- Forecasting Future HR Needs:
- Quantitative Methods: Techniques like trend analysis and regression models predict workforce requirements based on historical data.
- Qualitative Methods: Managerial judgment and the Delphi technique provide insights into future needs based on expert opinions.
- Gap Analysis: Identifying discrepancies between current capabilities and future needs allows for targeted interventions. This step is critical for understanding where training or recruitment efforts should be focused.
- Action Planning: Developing strategies such as recruitment, upskilling, internal mobility, or outsourcing addresses identified gaps. Organizations must prioritize actions based on urgency and impact.
- Monitoring and Evaluation: Setting Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) to measure success and periodically reviewing the HR plan ensures ongoing alignment with organizational goals. Continuous feedback loops help refine strategies over time.
Types of HR Planning
Different types of HR planning cater to various organizational needs:
- Workforce Planning: Focuses on short-term staffing and scheduling needs to ensure operational efficiency.
- Succession Planning: Ensures leadership continuity by preparing for key position vacancies through talent development.
- Strategic HR Planning: Aligns long-term talent management with corporate strategy to support overall business objectives.
Benefits of Effective HRP
Implementing effective HRP offers numerous advantages:
- Improved Talent Acquisition and Retention: HR Strategic planning attracts top talent while fostering employee loyalty through targeted development opportunities.
- Enhanced Employee Productivity and Satisfaction: A well-planned workforce leads to higher morale and engagement among employees.
- Better Risk Management During Organizational Changes: Proactive planning prepares organizations for transitions such as mergers or restructuring.
- Cost Optimization: By accurately forecasting staffing needs, organizations can avoid overstaffing or understaffing situations that lead to unnecessary expenses.
- Increased Agility: Effective HRP enhances organizational agility by enabling quick responses to changes in market conditions or business strategies.
Common Challenges in HRP and How to Overcome Them
Organizations often face challenges in implementing effective HRP:
- Inaccurate Forecasting Due to Market Volatility: To enhance forecasting accuracy, organizations should leverage data-driven decision-making techniques that incorporate real-time market insights.
- Resistance to Change Within the Organization: Fostering a culture of continuous communication can help ease transitions and encourage buy-in from employees.
Strategies such as training programs, workshops, and regular updates can facilitate smoother implementation of new HR initiatives.
Role of Technology in Modern HRP
Technology has revolutionized the way organizations approach human resource planning:
- HR Software and AI Tools: These tools facilitate efficient workforce planning by automating data collection and analysis processes.
- Predictive Analytics for Talent Forecasting: Advanced analytics help anticipate future workforce needs based on historical data trends.
Examples of popular HR tech solutions include:
- Applicant Tracking Systems (ATS) for recruitment management.
- Learning Management Systems (LMS) for employee training and development.
- Performance Management Systems (PMS) for tracking employee progress.
Case Studies: Successful HRP in Action
Several companies have successfully implemented strategic HR planning:
- Tech Giant Example: A leading IT firm anticipated a surge in demand for cloud services due to market trends. Through effective HRP, they identified a shortage of cloud architects early on, allowing them to implement targeted hiring initiatives alongside upskilling programs for existing employees.
- Manufacturing Company Case Study: A manufacturing company faced challenges during a merger that required a significant realignment of its workforce. By leveraging hr strategic succession planning, they ensured leadership continuity while addressing skill gaps through comprehensive training programs.
These case studies illustrate how proactive HRP practices can lead to successful outcomes even in challenging circumstances.
Conclusion
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Human Resource Planning (HRP) is the process of forecasting an organization’s future human resource needs and determining how to meet those needs effectively.
Effective HRP helps organizations align their workforce with strategic goals, improve productivity, reduce costs associated with turnover or understaffing, enhance employee satisfaction, and ensure compliance with labor laws.
Types include workforce planning (short-term), succession planning (leadership continuity), and hr strategic HR planning (long-term alignment with corporate strategy).
Technology streamlines processes through automation, predictive analytics for talent forecasting, applicant tracking systems for recruitment management, learning management systems for training employees, and performance management systems for tracking progress.
Organizations can utilize data-driven decision-making techniques for accurate forecasting while fostering continuous communication to ease transitions during changes in HR initiatives.
Take your business to the next level with smart Human Resource Planning! Streamline your workforce, boost efficiency, and drive growth. Start planning your success today!





